McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine
About
The McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine is the first Canadian textbook of internal medicine developed at McMaster University, the birthplace of problem-based learning (PBL) and evidence-based medicine (EBM) and one of the leading medical schools in the world, in collaboration with the Polish Institute for Evidence Based Medicine. Covering the essential fields of internal medicine, the textbook is aimed at answering the needs of medical professionals as well as residents and students who seek access to updated, verified medical knowledge useful in everyday practice.
The McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine is a practical, reliable, and easy to use resource tailored to the needs of physicians, trainees, and allied health professionals.
The McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine is unique thanks to the combination of contributions from expert authors, pragmatic approach employing the GRADE system, and accessibility.
Summary of the GRADE system application
GRADE stands for Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation.
Different information resources, such as textbooks and clinical practice guidelines, contain statements telling others what to do. These statements are recommendations. In this section, we describe the formulation and presentation of such recommendations in the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine. Our goal is to distinguish statements used when indicating the best course of action with complete certainty from statements that convey a lower degree of certainty.
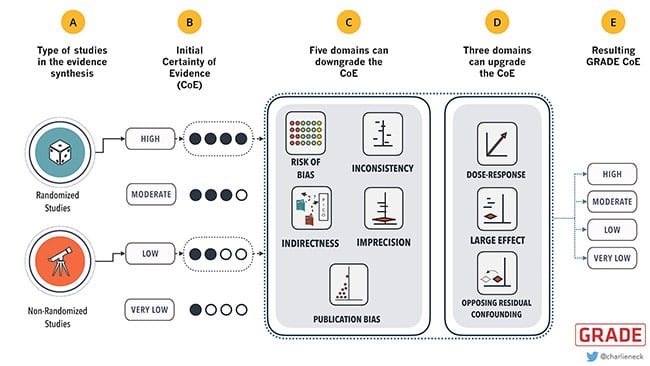

The body of evidence of 1 or more studies will start as high or low certainty of evidence (CoE), or quality of evidence (QoE), if it is composed of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or nonrandomized studies (NRS), respectively (A and B). There are 5 GRADE domains that can downgrade the CoE/QoE (C), while 3 will upgrade it when judged to be present (D). Based on these judgements a final CoE/QoE is obtained for the whole body of evidence for each outcome (E).
Note: Upgrading the CoE is only recommended for nonrandomized studies.
Definitions
Quality of Evidence (QoE) or Certainty of Evidence (CoE) is described as high through moderate to low and reflects our trust (confidence, certainty) that we know true effects of alternative interventions in terms of outcomes that patients consider important. The quality depends on the methodology of the underlying studies and includes:
- Risk of bias.
- Similarity of findings from study to study (homogeneity vs heterogeneity of findings).
- Precision of estimates.
- Directness of studies to the question of interest in terms of:
- Similarity of our patient(s) to the population studied.
- Similarity of interventions used to what we intend to use.
- Similarity of outcomes measured to what we want to accomplish.
- The likelihood of publication bias.
Strong recommendation is made when we are confident that following our recommendation will do more good than harm (all or almost all fully informed patients would choose the recommended action). The language used in such cases involves “we recommend,” “one should,” or imperative forms like “do it,” “use this drug.”
Weak recommendation (suggestion) is made when we are less confident in the given course of action (the majority of fully informed patients would choose the suggested course of action but a minority would not). The preferred language is “we/I suggest,” “one might,” or equivalent. Please note that making strong recommendations in the setting of low quality of evidence is rare.
Comparison of a statement of fact versus an actionable recommendation: Sometimes our goal is to present a fact rather than make a recommendation. As an example consider: “Impaired left ventricular function predicts poor prognosis” versus “Use medication X to improve left ventricular function.” Both types of statements may have QoE assigned to them to indicate how much we trust the underlying evidence.
Confidence in the recommendation/strength of recommendations: We express confidence/certainty through the language used to formulate recommendations. Apart from that, in the case of selected recommendations we also indicate confidence using appropriate symbols.
When deciding on the strength of recommendations, one needs to take into account the quality of the underlying evidence, the likely balance between desirable and undesirable consequences, variability in patients values and preferences (if relevant), and cost.
Electronic edition
The electronic edition of the McMaster Textbook is updated on the go. It can be accessed at mcmastertextbook.one or through the McMaster Textbook mobile app.
The digital content is tailored to practicing physicians and medical students seeking reliable information that is presented in an easily digestible format. Rather than aggregating as much as possible, the McMaster Textbook sifts through emerging research data to focus on the findings that are most likely to be of practical value.

An all-encompassing platform, the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine offers:
Over 800 textbook chapters, updated on the go and continuously expanded with new topics.
McMaster Perspective interview series, a collection of in-depth conversations that bring together the world’s leading medical experts and McMaster University’s renowned evidence-based medicine approach. Delivered in an engaging conversational format that makes complex topics accessible and memorable, the interviews often explore how medical “dogmas” have evolved over time, juxtapose guideline recommendations with real-life scenarios, and question what current practices might change in the coming decades.
Lectures from medical conferences, including the McMaster International Review Conference of Internal Medicine (MIRCIM)
McMaster Selects Journal Club, featuring critical reviews of carefully selected recent publications identified by McMaster University editors as most likely to impact clinical practice. Each review examines studies that may lead to practice-changing recommendations or otherwise influence the daily practice of medicine.
Internal Medicine Rapid Refreshers, helping you to quickly revise your knowledge of the conditions you are likely to encounter in your daily practice
Print edition


In October 2019, to mark the 50th anniversary of McMaster University’s Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine, the first print edition of the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine was released, accompanied by the launch of mobile applications for iOS and Android.
Spanning over 1500 pages and covering the essential fields of internal medicine, the textbook strived to answer the needs of physicians, residents, medical students, and other medical professionals who seek access to updated verified medical knowledge useful in everyday practice. It aims to be practical, current, and affordable.
Authors
The authors of the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine have extensive hands-on experience in treating patients around the world. Remarkably successful in translating this knowledge into practical instructions for other medical professionals, many have also participated in the development of clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements, which shape the modern medical practice. A significant number of our authors have been also involved in pioneering research and designed groundbreaking clinical trials that guide today’s clinical practice.
The Editorial Board can be found at mcmastertextbook.one.
Story behind the project
The origins of the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine can be traced back to Kraków, Poland, the home of the Jagiellonian University, which is one of the oldest medical schools in the world. The year 2005 saw the publication of Interna Szczeklika, an internal medicine textbook edited by the late Professor Andrzej Szczeklik, a renowned Polish physician and scientist. The textbook, written in accordance with the principles of EBM, has become the cornerstone of medical education in Poland, available in paper edition as well as a web-based textbook and a mobile app.
In 2014, the authors of Interna Szczeklika were joined by editors and contributors centered around McMaster University, the birthplace of evidence-based medicine. At subsequent stages, additional expertise was provided by clinicians from North America and Europe. The result of their collaboration is the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine. Expanded in scope and adapted with North American readers in mind, the textbook employs GRADE system indicators and offers a unique, pragmatic approach to internal medicine.
The ultimate goal of the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine is to create a comprehensive, reliable, up-to-date resource that will be useful to internists, all subspecialists, general medical practitioners, and medical students, both in ambulatory and in-patient settings.
With medical knowledge expanding all the time, our journey has only just begun. We invite you to join us not only by using the McMaster Textbook of Internal Medicine in your practice, but also by providing us with your feedback, pointing out potential omissions or inconsistencies, identifying needs for updates, and suggesting new features that you would find useful in your everyday practice.
Contact
If you have any comments, questions, ideas, or words of encouragement, our team is looking forward to hearing from you:
contact@mcmastertextbook.one
mcmastertextbook@piebm.org
Polish Institute for Evidence Based Medicine Foundation
ul. Gazowa 14A, 31-060 Kraków, Poland